

 |
 |
| Division of Earth Mechanics |
Monitoring method of seismic activity
Small changes in seismic activity such as activation or quiescence can be detected by our monitoring method based on statistical modeling. The significance of a change is measured by the difference of AIC between models with and without the change. The figure shows the AIC difference for decrease in b-value prior to the M6.4 Northern Miyagi earthquake of July 26, 2003.
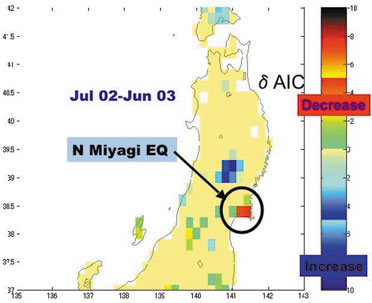
Seismic activity prior to the Miyagiken Hokubu earthquake (2003.7.26)
Integrated earthquake simulation on virtual city
Common recognition of possible earthquake hazards among citizens, government officers and earthquake engineers is important for urban disaster prevention. To form this common recognition, large-scale simulator of earthquake hazard on virtual city is being developed. This simulator consists of the large-scale simulation tools on fault mechanics, wave propagation through crust, wave amplification near ground surface and dynamic responses of structures and buildings of various types.
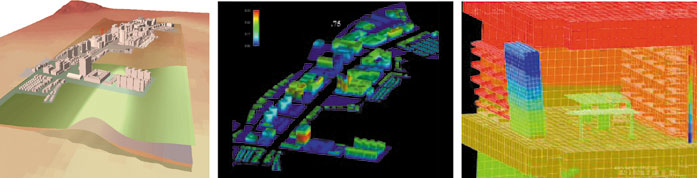
Prediction of the damage on the virtual city left: virtual city,
center: damage on the city, right furniture in a room
Prediction of seismic and volcanic activities with crustal deformation survey
On the mechanical and probabilistic viewpoints, seismic and volcanic activities are analyzed to find available methods for prediction. For example, predictions were being practiced to examine a hypothesis with respect to the activity of small earthquakes. In relation to this, a test of time-shift was proposed as a useful method of statistical eavaluation.
Resonance oscillations between the solid Earth and the atmosphere
In the Earth's background oscillations, there exists evidence of resonance of seismic free oscillations with acoustic waves. The resonant amplitudes suggest the atmospheric excitation of the acoustic waves but there is no direct observation of them. For detection of the long period acoustic waves, we installed cross array of barometers in University Forest in Chiba. The observation shows existence of acoustic waves with scale smaller than 100 km.
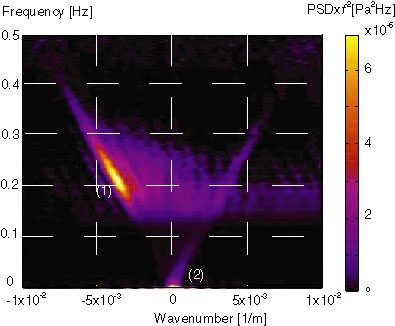
Resonance oscillations between the solid Earth and the atmosphere
Mechanical properties of solid-liquid composites
Mechanical properties of melt-bearing polycrystalline aggregates are studied both theoretically and experimentally. Experimental studies on the elastic, anelastic, and rheological properties of these systems were performed by using an analogue sample which partially melts near room temperature (a binary eutectic system of organic compounds). We established a practical method to derive quantitative information about porosity and geometry of the liquid pores existing in the Earth interiors from seismic tomographic images.

A reflected light micrograph of partially molten rock analogue
Generation of plumes in density-stratified layered fluid system
Our group has focused on behavior of thermal convection and plumes in the mantle dynamics based on laboratory experiments and numerical simulations. We are exploring how thermal plumes are generated in density-stratified layered fluid system in conjunction with the plume formation from D? layer in the deep mantle. The figure shows one instructive example where initially buoyant plume was disintegrated into 2 parts; thermal plume and compostional plume because of the entrained heavy fluid. This illustrates a lesson to the interpretation of tomography data.
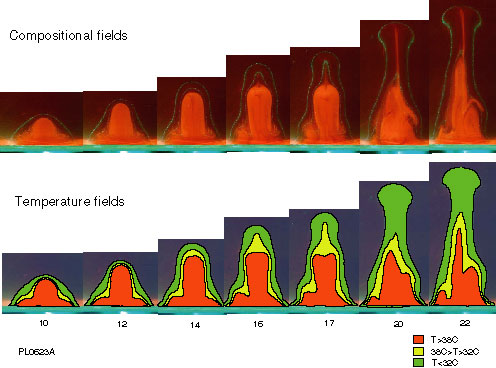
Example of plume disintegration (The upper figure represents composition
The red colored part is the lower dense fluid. The lower represents
temperature field.)
Noble gas geo/cosmo chemistry
Noble gases are useful tracers of physical processes because of their inert property. Isotopic compositions of noble gases in terrestrial and extra-terrestrial materials are analyzed with mass spectrometers in order to study their origins, mechanism of magmatic differentiation processes, thermal histories, and surface erosion rates. Chronological studies based on K-Ar and Pu-Xe methods have also been carried out for clarifying volcanism and planetary formation