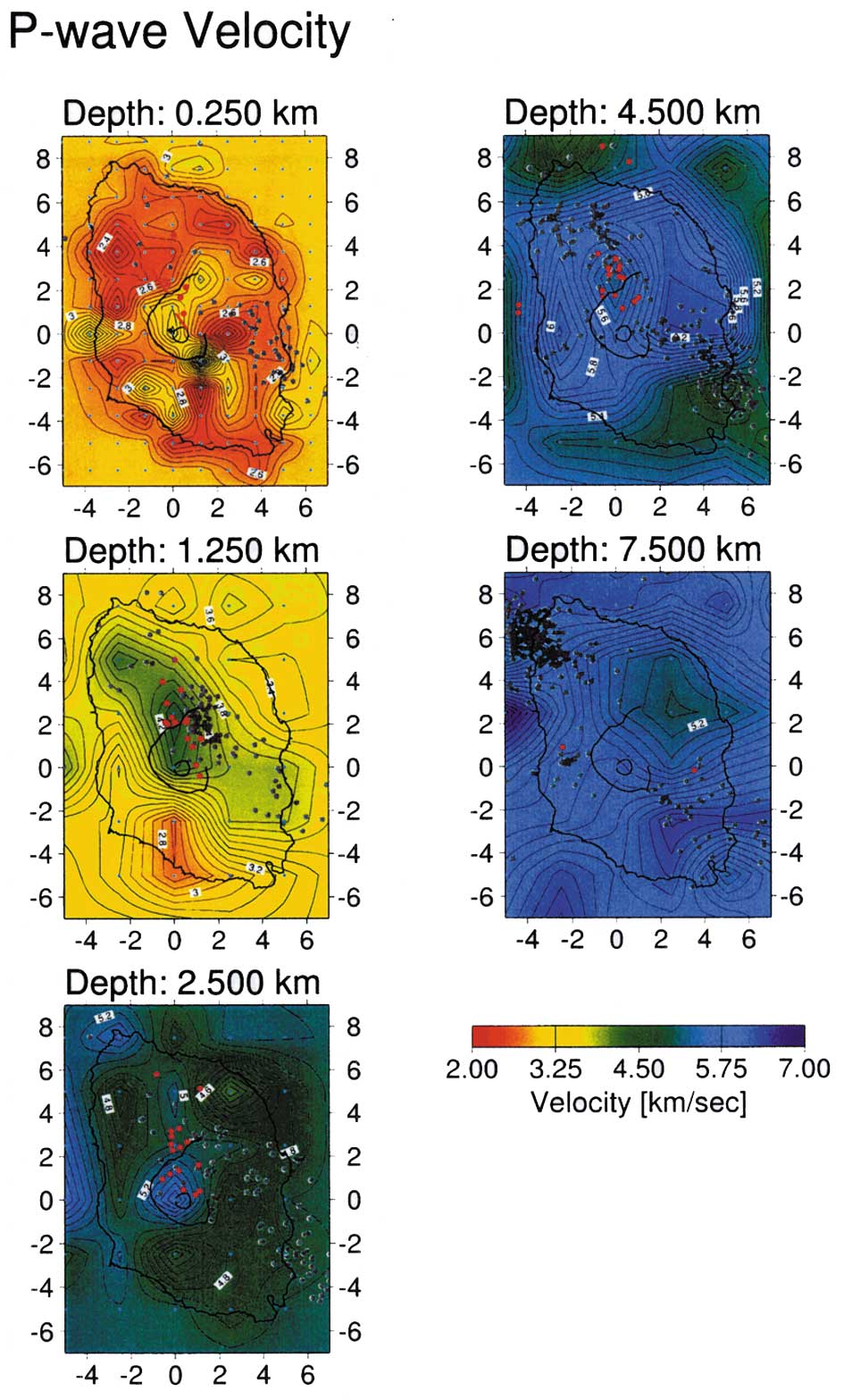
Seismic explosion experiments succeed to determine a precise velocity
structure up to 3km in depth
by high-density observation network and newly developed seismic tracing
method. In recent years, new
method, which combines teleseismic and gravity data, succeeded in detecting
some anomalous regions
related to magmatic activity in Izu-Oshima Volcano (Fig.2).
Electromagnetic survey found that the deep low resistivity region
about 10 km below the surface, and
the shallow low resistivity region about 1 km below the surface. Shallow
low resistivity region, which is
interpreted as a water-saturated porous layer, plays an important role
in controlling types of eruption
and in generating precursory phenomena of volcanic eruptions.
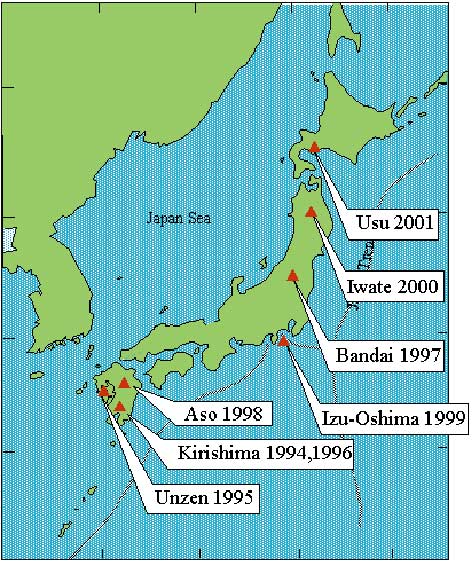
Fig.1. Joint volcanological experiment on volcanic structure
and magma supply system
in Japan.